What Is Prebiotic Food? And Why You Need Them.

What Are Prebiotics?
A particular type of specialized plant fiber called prebiotics helps your gut’s microbes thrive and promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria. Complex carbohydrates, such as fiber and starch, are present in fruits and vegetables. Because your body is unable to digest these carbohydrates, they pass through the digestive tract and into your colon, where the microbes in your gut break down and ferment theprebiotics rich foods. Various short-chain fatty acids are produced during the breakdown of prebiotics. By giving your colon cells energy, generating the required mucus, lowering inflammation, and boosting immunity, these short-chain fatty acids enhance your metabolic and general health. To put it briefly, consider prebiotics to be the fertilizer that promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
All of the amazing facts and tales you may have heard about prebiotic food are accurate! Foods that include prebiotics are fantastic for digestion and general health. They provide you with good bacteria that improve digestion and strengthen your immune system.
For more information about prebiotic foods and their amazing health benefits, please read the blog byGwellth! You must be prompted to include them in your regular diet. So, let’s get started.
Your gut flora loves prebiotic foods, which are a type of nutritional fiber that your body cannot process. Furthermore, as a healthy gut is the cornerstone of overall well-being, prebiotics are beneficial for digestion and general health.
Prebiotic meals can be great allies if you want to strengthen your immune system, enhance your digestion, or lessen inflammation by consuming beneficial microorganisms.
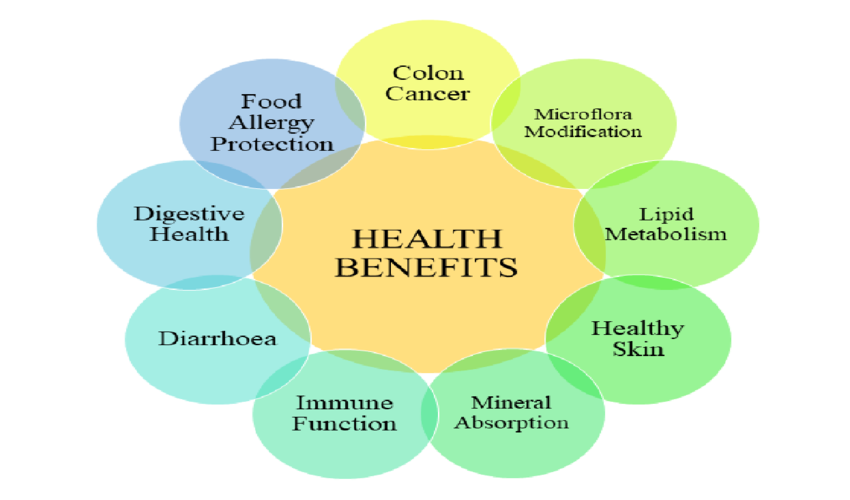
Health Benefits Of Prebiotic Foods
The advantages of prebiotics are extensive and influence various aspects of health beyond mere digestive function. Studies indicate that prebiotics may:
- Enhance digestive health and metabolic processes.
- Assist in the regulation of bowel movements.
- Facilitate improved calcium absorption and promote increased bone density.
- Aid in the regulation of blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Encourage the secretion of hormones that contribute to appetite control.
- Reduce inflammation throughout the body.
- Boost the immune response.
- Support the balance and maintenance of hormone levels.
- Decrease the likelihood of allergic reactions.
- Reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Help regulate mood and lower levels of stress hormones.
- Reduce cholesterol levels.
- Lower the risk of developing colon cancer.
- Prebiotics And Digestive Health
Prebiotic food rich in fiber enhances digestive health by nourishing beneficial gut bacteria. In simple terms, prebiotics facilitate quicker food fermentation, thereby decreasing the time food spends in the digestive tract. This not only alleviates constipation but also promotes overall digestive efficiency. Furthermore, prebiotics aid in calcium absorption, support the health of gut lining cells, and enhance metabolic function. Therefore, incorporating prebiotics into your diet is undoubtedly a good choice.
- Prebiotics For Hair And Skincare
Prebiotic food is rich in antioxidants that safeguard the skin from damage inflicted by free radicals. These antioxidants contribute to improved skin texture, reduced inflammation, and a diminished appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Prebiotics play a significant role in maintaining the shine and smoothness of your hair and skin. They contribute to the regulation of pH balance, assist in acne management, and help address signs of aging, thereby enhancing the overall appearance of your skin.
Prebiotic foods are readily available in Indian Cuisine, it is fortunate that numerous options are available. Thus, sustaining a diverse and healthy gut microbiota is achievable with a few dietary variations.
- Enhances Nutrient Absorption
A prevalent gastrointestinal (GI) alteration associated with ageing is the decline in the gut’s absorptive capacity, leading to malnutrition, nutrient deficiencies, and malabsorption of essential micronutrients, which can result in severe health issues. Increasing evidence suggests that prebiotics may enhance the absorption of micronutrients, such as calcium and iron, from food. Studies indicate that these substances can improve nutrient bioavailability and overall nutritional status in older adults.
- Promotes GUT Microbiome Health
Individuals are born with a diverse gut microbiome that plays a crucial role in gastrointestinal health and immune function. However, this diversity tends to decrease with age due to various factors, including antibiotic usage, illnesses, infections, hormonal changes, circadian rhythm disruptions, and poor dietary habits. Consequently, the composition and functionality of gut microbes evolve over time. Therefore, the regular consumption of prebiotics is vital for gut bacterial diversity to sustain and enhance the population of beneficial bacteria, thereby supporting digestive health.
- Maintain Intestinal Integrity
The integrity of the intestines, referring to the preservation of their structure and function, is essential for maintaining overall health. Prebiotics can assist by increasing the abundance of beneficial microbial communities and inhibiting the growth of harmful pathogens that may damage the intestinal walls and disrupt digestive processes.
- Reduces Gut Inflammation
Research indicates that prebiotics may facilitate healthy ageing by alleviating inflammation within the gut. Incorporating prebiotics into the daily diet can enhance gut barrier integrity against inflammatory responses, combat pathogens, and provide relief from conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease.
- Enhances Metabolism And Weight Control
Individuals who incorporate foods rich in prebiotics tend to exhibit superior gut microbiota and metabolic performance compared to those who rely on processed and nutritionally deficient diets. Prebiotic-rich foods facilitate the breakdown of indigestible dietary fibers into short-chain fatty acids, which effectively regulate appetite and energy expenditure.
- Boost Immune System Function
While prebiotics are widely recognized for their role in promoting digestive health, research also highlights their significance in bolstering the immune system. It is noteworthy that our innate immunity is largely situated within the gut, serving as the primary defense against harmful microorganisms.
- Promotes Overall Well-Being
A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for maintaining digestive harmony, and prebiotics are known to restore this balance by altering the gut bacterial composition. They encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria that outnumber harmful pathogens, positively influencing various bodily systems. The gut microbiota plays a vital role in numerous digestive and metabolic processes, including the breakdown of bile and the prevention of its reabsorption, which is particularly beneficial for managing cholesterol levels. Prebiotics are especially important for women undergoing menopause, as they help maintain digestive efficiency, which may decline during this phase. Furthermore, the issues of malnutrition and nutrient absorption in the elderly can be alleviated through the use of prebiotics.
Prebiotics offer numerous advantages and are crucial for sustaining gut health, which in turn enhances overall well-being. With a wide array of prebiotic-rich food options available, you can identify the sources that are most suitable for your digestive system. Your gut, along with your entire body, will express gratitude for this attention to your dietary choices.
Conclusion
Prebiotic foods can be seamlessly incorporated into the diet. In India, a variety of options such as jaggery, honey, Indian millet and whole grains like brown rice are easily accessible. All of these serve as outstanding sources of prebiotic nutrients.
Prebiotic foods are natural components that are not digestible and serve to enhance the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria, known as probiotics. These foods are generally high in fiber, particularly in forms such as inulin, fructooligosaccharides, and galactooligosaccharides.
Incorporating prebiotic foods into one’s diet is vital for sustaining a balanced gut microbiome. A well-functioning gut microbiome is essential for effective digestion, immune system performance, and even mental well-being, as gut bacteria generate important nutrients, including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Additionally, prebiotics can enhance nutrient absorption, regulate bowel movements, reduce inflammation, and boost the body’s defense against infections.
FAQs
Question 1. What are the potential consequences of excessive consumption of prebiotic food?
Answer: Excessive intake of any food can lead to negative effects. While prebiotic meals themselves may not inherently cause harm, overconsumption can result in discomfort such as bloating, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal issues. It is advisable to allow the gut time to adjust; beginning with a moderate portion or a small serving of a preferred prebiotic fiber food and gradually increasing the amount is recommended.
Question 2. Can prebiotic foods contribute to weight loss?
Answer: Research indicates that prebiotic foods can facilitate weight loss by enhancing satiety and reducing overall caloric intake. Additionally, they promote gut health, which can further support weight loss efforts and improve metabolic function.
Question 3. How do prebiotic foods differ from probiotic foods?
Answer: The distinction between prebiotics and probiotics lies in their functions and characteristics. Both contribute to the maintenance of beneficial bacteria and organisms within the gastrointestinal tract, thereby facilitating digestion, yet they operate in distinct manners. Probiotics consist of live microorganisms, primarily specific strains of bacteria and yeasts, which are present in certain foods and enhance the existing microbial population in the gut. In contrast, prebiotics are dietary fiber (non-living food components) that occur naturally. They provide nourishment for probiotics, enabling their growth and activity. Consequently, the effectiveness of probiotics in promoting and sustaining gut health is dependent on the presence of prebiotics.